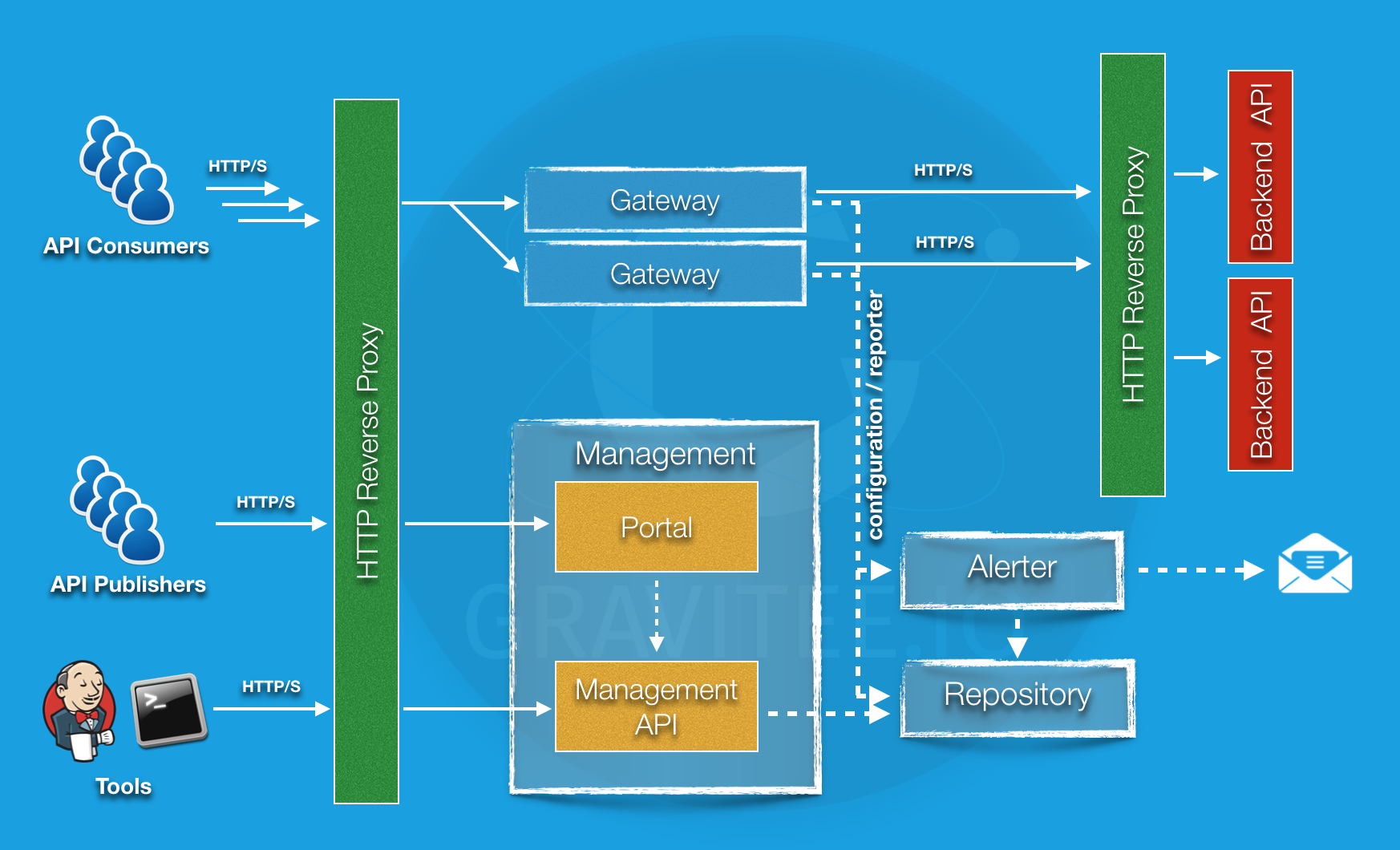
End-to-End API deployment
As a dev, I want to focus on my business application.
In this guide, we’ll be using Domain name, ACME protocole, Kubernetes, OVH API and few other products such as Elastic Search index, NOSQL database and Gravitee.io.
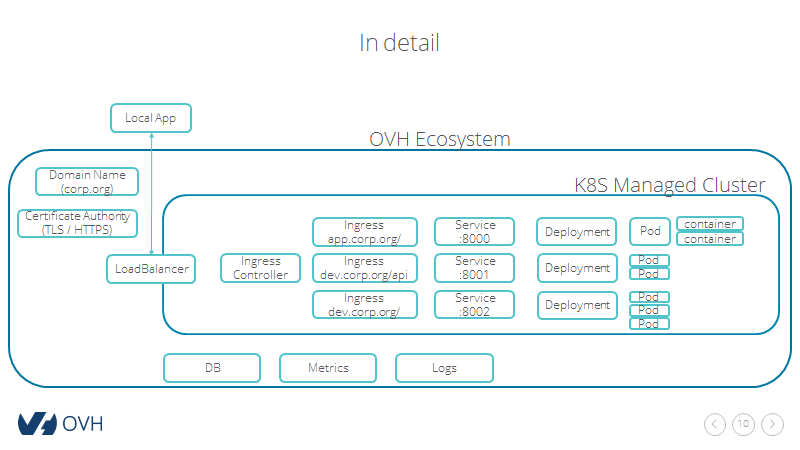
Kubernetes setup
Setup your local environment, add nodes and configure Helm.
. ./activate
Install the IngressController
First thing first, we’ll deploy a LoadBalancer and NGINX IngressController with helm.
You’ll be using this chart and deploy it in the kube-public namespace.
helm install stable/nginx-ingress --namespace kube-public --set controller.replicaCount=2
Domain and certificates
DNS config
Once the IngressController is up, you should get its ip and domain via kubectl -n kube-public get svc -l component=controller
kubectl -n kube-public get svc -l component=controller
Using the above value, edit your DNS Zone accordingly via the OVH Manager
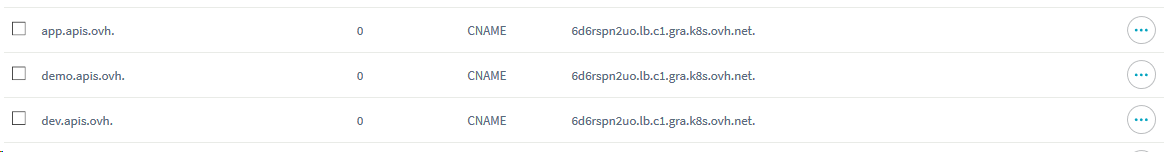
or via the OVH API
- with
POST /domain/zone/{zoneName}/importto import the entire DNS zone - with
POST /domain/zone/{zoneName}/recordto edit only entry.
Tip: To avoid waiting DNS config to propagate to your DNS servers - up to 24h -, set your DNS servers to OVH ones.
Certificates
Once your DNS zone is up. You can generate TLS certificate follwing the ACME DNS protocole.
Unlike with HTTP protocol, you’ll be able to generate certificate for wildcard sub-domain and without editing your web server configuration.
We strongly recommend to follow this guide which leverate OVH API and can be easilly automated.
After following the guide, you should generate the certificate with acme.sh --issue --dns dns_ovh -d '*.apis.ovh' from your local console.
You should obtain the following files:
domain.key: the domain private keydomain.csr: the domain certificate signing requestdomain.cer: the domain public keyca.cer: the certificate authority public keyfullchain.cer: the fullchain (CA + subordinate + your domain) public key
Let’s create a kubernetes.io/tls secret
kubectl create secret tls apis.ovh-cert --key ./domain.key --cert ./fullchain.cer
kubectl describe secret apis.ovh-cert
Install Gravitee.io
gravitee.io is an API manager. The setup is described here
Install Linkerd
The following commands are detailed here
linkerd check --pre && (linkerd install | kubectl apply -f -) # do a pre-check and install
linkerd check # check installation went fine
You can open a tunnel to access Linkerd dashboard. Run the following command in a separate termminal
linkerd dashboard
Once linkerd is installed and configured, only an extra step is needed for the Ingress. In our case with NGINX, we have to follow this documentation
kubectl get deploy -o yaml | linkerd inject - | kubectl apply -f - # to install Linkerd
kubectl annotate ing gravitee-ui 'nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/upstream-vhost=$service_name.$namespace.svc.cluster.local'
kubectl annotate ing gravitee-api 'nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/upstream-vhost=$service_name.$namespace.svc.cluster.local'
kubectl annotate ing gravitee-gateway 'nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/upstream-vhost=$service_name.$namespace.svc.cluster.local'
To remove the annotations
kubectl annotate ing gravitee-ui nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/upstream-vhost-
kubectl annotate ing gravitee-api nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/upstream-vhost-
kubectl annotate ing gravitee-gateway nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/upstream-vhost-